Informing diagnosis. Clarifying patient management.
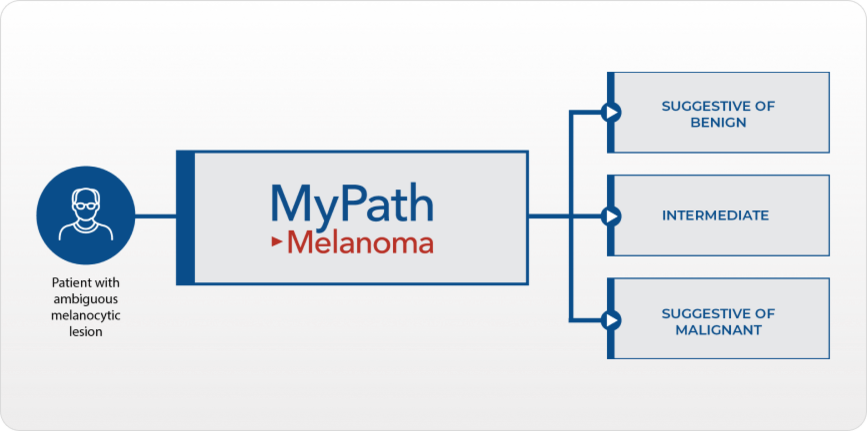
MyPath Melanoma gene expression profile (GEP) test is designed to provide objective information to aid in the diagnosis and inform management decisions for patients with ambiguous melanocytic lesions.
More clarity, less ambiguity
Watch the video to learn more about how gene expression profile (GEP) testing can provide objective information to aid in the diagnosis of ambiguous melanocytic lesions.


Microscopic analysis isn't always enough
An objective solution for lesions of uncertain malignant potential
MyPath Melanoma is designed to reduce uncertainty and reach a definitive diagnosis as quickly as possible to inform important patient management decisions regarding primary treatment and follow up.
MyPath Melanoma was validated in cutaneous melanocytic lesions to accurately differentiate between benign and malignant melanocytic lesions of unknown potential based on the expression of 23 genes.
Hear how Clay Cockerell, MD uses MyPath Melanoma in his practice
Examples of cases that are appropriate for testing
Case Studies
Guidelines support ancillary diagnostic testing in ambiguous melanocytic lesions
APPROPRIATE USE CRITERIA FOR ANCILLARY DIAGNOSTIC TESTING IN DERMATOPATHOLOGY
The ASDP’s appropriate use criteria committee has designated six key clinical scenarios in dermatopathology as "majority usually appropriate" for ancillary diagnostic GEP testing. These scenarios include melanocytic lesions in adult and pediatric patients for which a distinction between benign melanocytic nevi and melanoma cannot be made.
GUIDELINES FOR CUTANEOUS MELANOMA PRINCIPLES OF MOLECULAR TESTING
The NCCN guidelines direct physicians to consider the use of molecular testing, including GEP, in melanocytic lesions that are equivocal by histopathology. These tests facilitate a more definitive diagnosis and guide treatment decisions in lesions that are diagnostically ambiguous.
GUIDELINES OF CARE FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF PRIMARY CUTANEOUS MELANOMA
The AAD supports the use of ancillary diagnostic molecular techniques (e.g., GEP, CGH, FISH) for equivocal melanocytic neoplasms. These tests may help to differentiate benign nevi from cutaneous melanoma, including atypical Spitz tumors.
Use of molecular testing to diagnose ambiguous melanocytic lesions
The SCPWG advocates for the use of GEP tests to distinguish between benign and malignant melanocytic lesions. This recommendation is based on the evidence that has shown GEP to improve key diagnostic parameters compared to histopathology alone.
Ready to incorporate GEP into your diagnostic workflow?
Learn more about how to order a MyPath Melanoma test at your practice.


View a sample report to see how MyPath Melanoma can inform diagnosis
Connect with a representative to learn more about MyPath Melanoma
- Cassarino et al. J Med Econ 2014.
- Lee et al. JAAD 2017.
- Gelbard et al. JAAD 2002.
- Fleming et al. JAAD 2020.
- Strazzula et al. JAAD 2014.
Copyright ©2024 Castle Biosciences