Case Study
Concerning melanocytic lesion in patient with personal history of melanoma
A 49-year-old male was seen by a dermatologist for a concerning nevus on the right superior lateral neck. The patient's age, extensive solar damage, and history of metastatic melanoma was a cause for concern.
Case details
The patient presented an atypical lentiginous junctional melanocytic proliferation consistent with de novo epithelioid melanocytic dysplasia on his right superior neck. The patient has a history of extensive sun damage and has had metastatic melanoma in the right parotid gland with oligometastatic disease of the CNS with an unknown primary.
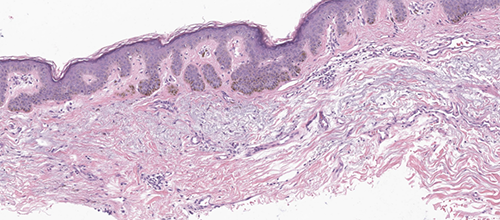
Original and multiple deeper levels of the block demonstrate a shave biopsy of actinically damaged skin, showing an irregular epidermal acanthosis with elongation of the rete ridges and hyperpigmentation of the basal keratinocytes. Melan-A and Sox-10 demonstrate a background of increased melanocytic density consistent with solar lentigo.
In addition, the lesional center shows ~3 mm area of confluent melanocytic growth. The individual melanocytes in this area demonstrate a low-grade epithelioid atypia. No dominant pagetoid spread or melanocytic nests identified. In sum, the overall morphological impression is that of a de novo epithelioid melanocytic dysplasia arising on a background of solar lentigo; however, diagnostic criteria for lentigo maligna are not fulfilled. The area of dysplasia is ill defined but appears to be completely excised with approximately 2mm negative margin. No dermal melanocytes identified.
The pathology finding were abnormal but did not meet the diagnostic threshold for a melanoma diagnosis. Given the abnormalities noted and the patient's history of metastatic melanoma, diagnostic GEP testing was ordered.
GEP results were suggestive of malignant neoplasm. The case was subsequently sent for a second opinion consultation and was found to have a focal area suspicious for melanoma in-situ.
Following the test result, the treatment plan was modified and a wide local excision was performed with more appropriate margins.
Diagnostic GEP testing providedvaluable objective informationto the dermatologist and&helped guide treatment planning